Pipeline
We Are Building a Deep Pipeline.
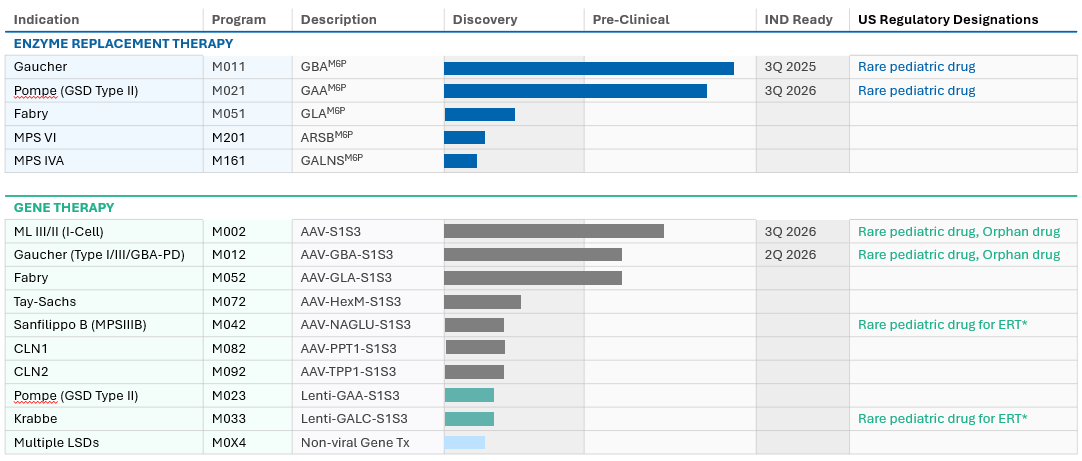
Enzyme Replacement Therapies and Gene Therapies
We have promising preclinical data across numerous LSD programs for both enzyme replacement therapies (ERTs) and gene therapies. Our lead programs are Pompe disease, Gaucher disease, Fabry disease, and mucolipidosis (ML), and we plan to initiate our first clinical program in 2023.
Our platform candidates show the characteristics of promising drug candidates, including:
- Greater affinity for binding for the key M6P receptor on the cell surface, which leads to superior targeting to tissues
- Superior cellular uptake with efficient lysosomal delivery
- Active within lysosome and successful in breaking down the substrate
Preclinical Data: What We’ve Seen to Date
Our lead investigational drug candidates hold strong promise of becoming either first-in-class or best-in-class treatments.
M021 Program
A next generation recombinant human acid α-glucosidase (rhGAA) ERT for Pompe disease. Preclinical data include:
M021 Pompe ERT is naturally produced with the highest levels of M6P as compared to other rhGAA ERTs
M021 has very high binding affinity for the intended cation-independent M6P receptor (CI-MPR)
M021 is efficiently internalized into fibroblast cells derived from individuals with Pompe disease and muscle myoblast cells via the CI-MPR pathway
M021 has significantly better muscle targeting in Pompe mice than standard of care ERT
M021 contains all natural bonds on glycans which enables proper processing and enzyme activation for optimal activity in lysosomes
M021 is substantially better than standard of care ERT glycogen for substrate clearance in muscles of Pompe mice
M021 normalized glycogen and significantly improved muscle strength in Pompe mice in long-term studies
M011 Program
A next generation recombinant human β-glucocerebrosidase (rhGCase) ERT for Gaucher disease. Preclinical data include:
The only Gaucher ERT with high levels of M6P to enable high affinity binding to the cation-independent M6P receptor (CI-MPR)
M011 has markedly increased uptake into fibroblast cells derived from individuals with Gaucher disease
M011 has a much more favorable pharmacokinetics profile and much broader tissue distribution than currently approved ERTs in Gaucher mice
M011 shown to have superior cellular uptake and substrate clearance in all key target tissues & cells including in bone and bone marrow as compared to standard of care imiglucerase under identical experimental conditions
M011 is well tolerated at very high doses with no observed adverse findings in IND-enabling toxicity studies
M011 shown to have efficient uptake and broad distribution of M011 in brain when administered directly into the CNS
We are evaluating different routes of administration to deliver M011 into CNS for developing a potential treatment for Type 3 Gaucher disease
M012 Program
A novel gene therapy approach for Gaucher disease and potentially GBA1-Parkinson. Preclinical data include:
The only gene therapy that ensures production of human β-glucocerebrosidase (hGCase) with high levels of M6P in vivo
Produced highly phosphorylated GCase shown to have high affinity binding to the intended cation-independent M6P receptor (CI-MPR) in vitro which enables efficient cellular uptake in vivo
Highly phosphorylated GCase produced from AAV gene therapy has broad tissue distribution for cross-correction of non-transduced cells since CI-MPR is expressed on nearly all cells
Effective substrate clearance in key target tissues in the periphery
M012 has the potential for cross-correction in the CNS since CI-MPR is present and utilized for uptake of phosphorylated lysosomal enzymes
M012 is being developed as a new treatment for Type 3 Gaucher disease and potentially for GBA1-linked Parkinson disease
M052 Program
a novel gene therapy approach for Fabry disease. Preclinical data include:
The only gene therapy that ensures production of α-galactosidase A (α-Gal A) with high levels of M6P in vivo to enable high affinity binding to the cation-independent M6P receptor (CI-MPR) for efficient cellular uptake
Highly phosphorylated α-Gal A shown to be better targeted to key tissues as compared to WT α-Gal A
Highly phosphorylated α-Gal A has superior substrate clearance in key target tissues as compared to WT α-Gal A under identical experimental conditions in Gla knockout Fabry mice
M002 Program
a novel gene therapy approach for Mucolipidosis II & III (ML II/III). Preclinical data include:
ML II mouse model has absent Phosphotransferase (PTase) activity such that ALL soluble lysosomal enzymes lack M6P and are hyper-secreted into the bloodstream with very low levels in tissues
M002 S1S3 PTase AAV gene therapy restores phosphorylation of soluble lysosomal enzymes within transduced cells within 3 weeks after dosing
Produced phosphorylated lysosomal enzymes have high affinity for the cation-independent M6P receptor CI-MPR in vitro
Significantly higher levels of phosphorylated lysosomal enzymes are distributed into broad set of tissues post-dosing
M002 gene therapy shown to reduce various accumulated substrates and vacuoles in key tissues in ML II
M002 gene therapy-treated ML II mice shown to improve functional and cognitive endpoints in long-term studies
Early Discovery Programs
Comprise of initial evaluation of the M6PT phosphorylation technology to increase M6P levels for different lysosomal enzyme targets. Preclinical data include:
Characterization of M6P levels and CI-MPR binding for wildtype lysosomal enzymes
Evaluation of S1S3 PTase co-expression to increase M6P levels and improve CI-MPR binding affinity for various soluble lysosomal enzymes
Co-expression of S1S3 PTase shown to significantly increase M6P levels and improve CI-MPR binding for vast majority of lysosomal enzymes
Applying learnings for developing improved ERTs for treating peripheral manifestations and gene therapies for diseases with CNS manifestations

